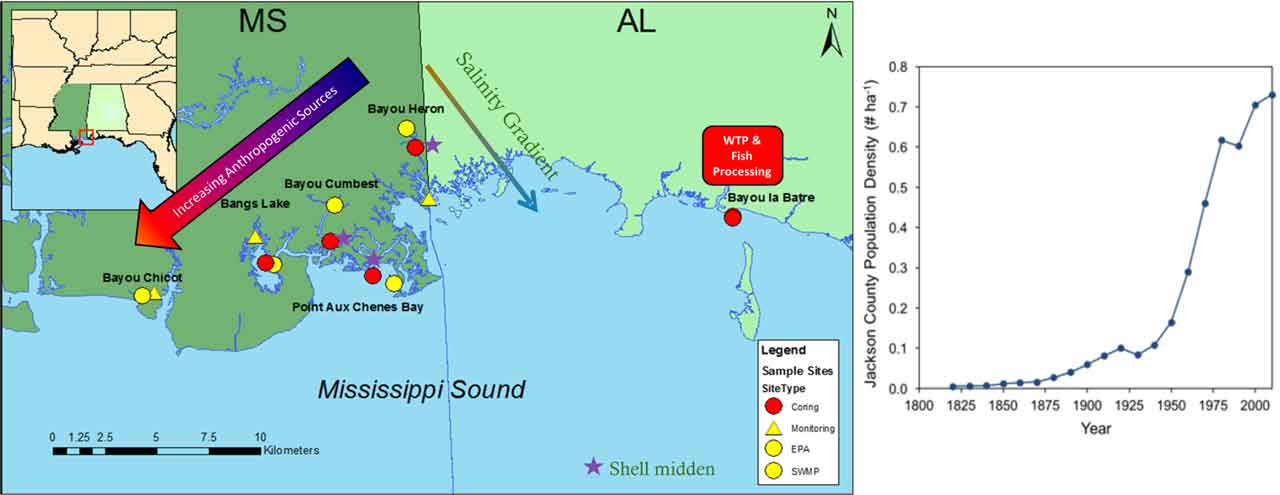
Grand Bay is one of the largest estuaries on the Mississippi-Alabama coast, in one of the most underserved regions in terms of science, technology, and education. Much of the regional income and recreation is water-dependent, including commercial fishing, fish processing, and a burgeoning eco-tourism industry.
Grand Bay is also part of the National Estuarine Research Reserve (NERR) system and is one of the youngest and least studied NERR sites in the country. Hence, there is a need for publicly available information about human effects on local resources to support decision-making about land use planning and other ways to protect and improve water quality.
History of human activity in Grand Bay
Human population in the Grand Bay region increased after the Civil War due to logging and shipbuilding industries. In the 1950s and 1960s, marshes and shorelines were altered to develop the Port of Pascagoula and the chemical industries between Bayou Casotte and Bangs Lake. Jobs accompanying these industries led to a human population explosion from the 1950s-1980s.
Wastewater treatment plants were installed to the west (Pascagoula, Moss Point) and east (Bayou la Batre) mid-century, for primary treatment of human wastewater, but many homes in the Grand Bay area remain on septic systems.